what is polar or nonpolar molecule Nonpolar molecules molecule differences substance atoms
Polar vs Nonpolar Molecules: What’s the difference? Have you ever wondered why some substances dissolve in water while others do not? Why do oil and water not mix? The answer lies in the polar and nonpolar nature of molecules. First, let’s define what we mean by polar and nonpolar molecules. A molecule is said to be polar if it has a positive and negative end or pole. Nonpolar molecules, on the other hand, do not have such opposite poles. One of the key differences between the two is their behavior when it comes to intermolecular forces. Polar molecules can form hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules, making them more likely to dissolve in polar solvents such as water. Nonpolar molecules, on the other hand, can only form weak London dispersion forces with other nonpolar molecules and are therefore more likely to dissolve in nonpolar solvents such as oil. Let’s take a closer look at some examples. Water is a polar molecule because it has a partial positive charge on its hydrogen atoms and a partial negative charge on its oxygen atom. This polarity allows water molecules to interact with each other through hydrogen bonding, making it a good solvent for polar substances such as salt or sugar. In contrast, oil is a nonpolar molecule because it has no opposite poles. This makes it insoluble in water because water molecules cannot interact with it through hydrogen bonding. Another example of a polar molecule is ammonia (NH3). It has a partial positive charge on its hydrogen atoms and a partial negative charge on its nitrogen atom, making it able to form hydrogen bonds with water. On the other hand, methane (CH4) is a nonpolar molecule because it has no opposite poles, making it insoluble in water. Knowing the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules is important, as it can help us understand their behavior in different environments. For example, in biology, the polar nature of water is essential for many biological processes. It allows for the formation of hydrogen bonds between water molecules, which gives water unique properties such as high surface tension, high boiling point, and high specific heat capacity. In conclusion, the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules lies in their polarity and behavior in different environments. While polar molecules can interact with other polar molecules through hydrogen bonding, nonpolar molecules can only form weak London dispersion forces with each other. Understanding these differences can help us understand the behavior of substances in different solvents and environments.
If you are searching about Polar vs Nonpolar Molecules- Definition, 7 Key Differences, Examples you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Pictures about Polar vs Nonpolar Molecules- Definition, 7 Key Differences, Examples like Difference Between Polar and Nonpolar Molecules | Definition, Formation, Polar vs Nonpolar Molecules- Definition, 7 Key Differences, Examples and also Polar Molecules | Chemistry for Non-Majors. Read more:
Polar Vs Nonpolar Molecules- Definition, 7 Key Differences, Examples
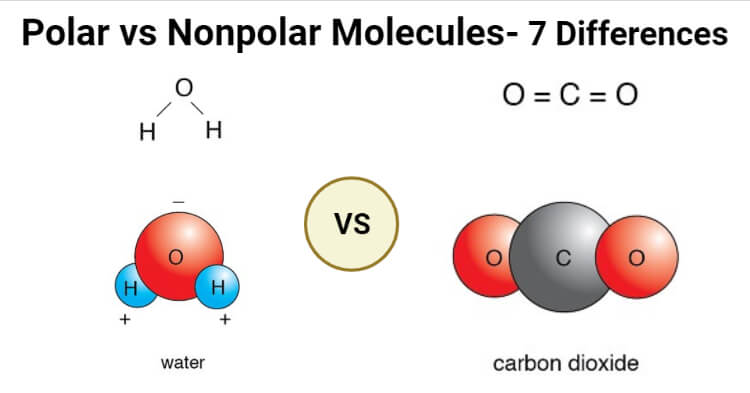 thechemistrynotes.comnonpolar molecules molecule differences substance atoms
thechemistrynotes.comnonpolar molecules molecule differences substance atoms
Polar And Nonpolar Molecules
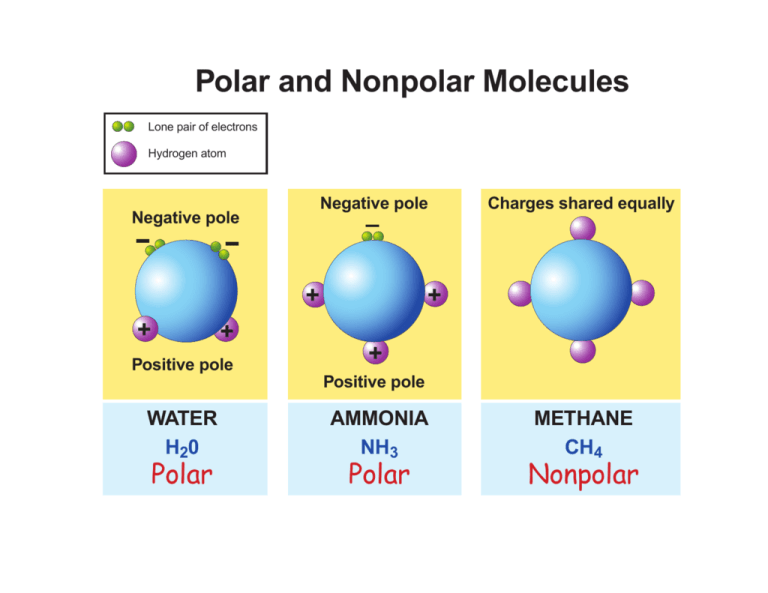 studylib.netnonpolar molecules nh3 ch4 molecule atom bonds solved atoms studylib
studylib.netnonpolar molecules nh3 ch4 molecule atom bonds solved atoms studylib
Polar Molecules | Chemistry For Non-Majors
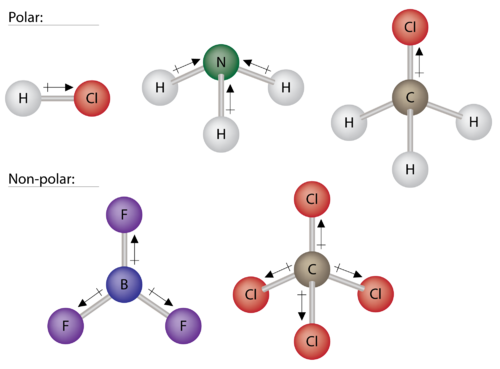 courses.lumenlearning.compolar molecules nonpolar examples non molecular geometry chemistry based figure majors some
courses.lumenlearning.compolar molecules nonpolar examples non molecular geometry chemistry based figure majors some
Difference Between Polar And Nonpolar Molecules | Definition, Formation
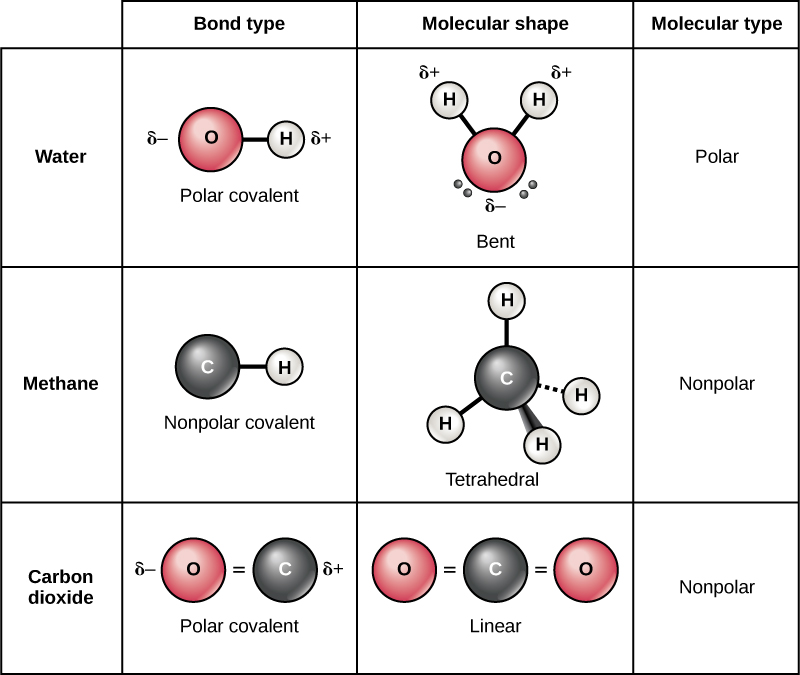 pediaa.compolar nonpolar molecules between difference examples definition properties dipole
pediaa.compolar nonpolar molecules between difference examples definition properties dipole
Polar And Nonpolar Molecules
 sciencenotes.orgnonpolar molecules covalent chemistry bonding
sciencenotes.orgnonpolar molecules covalent chemistry bonding
Polar molecules nonpolar examples non molecular geometry chemistry based figure majors some. Nonpolar molecules molecule differences substance atoms. Polar molecules